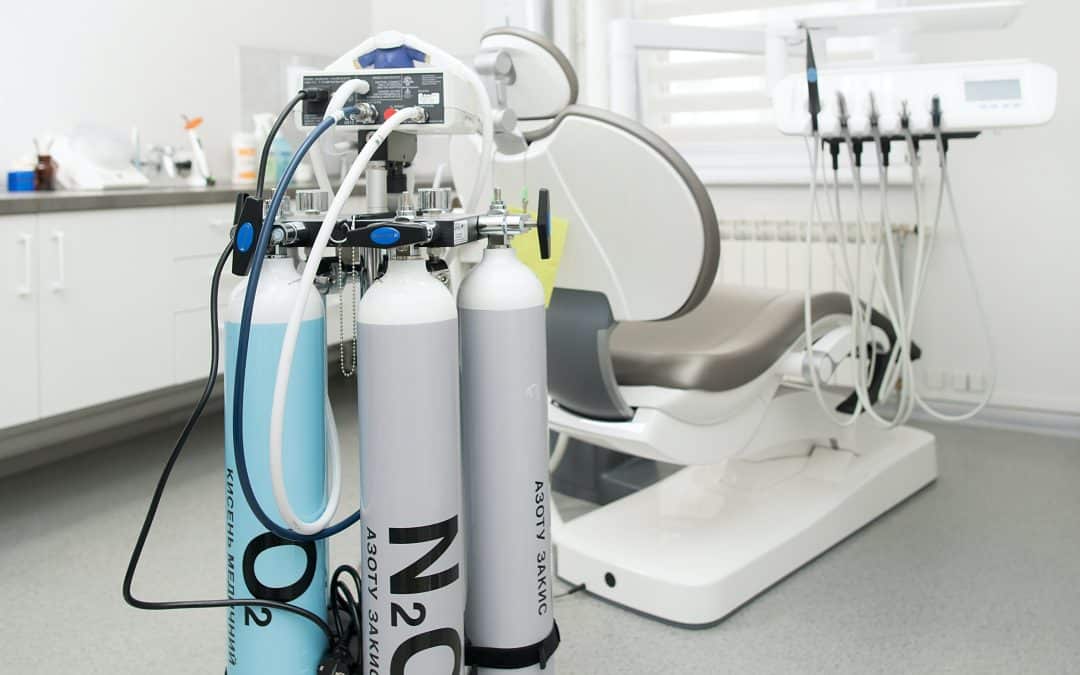
Whether used within a medical oxygen set-up or another type of system, medical gas valves are crucial to the operation of healthcare facilities across the country and the world. If these vital pieces of equipment are damaged, become blocked, or start to malfunction, the results can be dire.
Of course, medical facilities and healthcare institutions need to protect their investments, as well as the health, safety, and quality of care for patients. This means keeping gas tank valves in good working order, ensuring that they keep on functioning at their best for longer. To achieve this, managers and personnel can adopt a few best practices, designed to protect medical valves.
Pay Attention to Reasonable Usable Lifetime
Before we get into best practices aimed at extending the longevity of the valve without compromising on care, there is an important fact to consider – the lifespan of the valve cannot be extended indefinitely. There will be a limit on how long you can deploy your valves, and this is known as the Reasonable Useful Lifetime, or RUL.
The RUL will vary depending on the make and model of the valve itself, so it’s a good idea to keep hold of the guidelines and information supplied by the manufacturer. However, you can expect to need to change most valves after a period of around five years.
Work with Certified Installers and Maintenance Professionals
It is crucial that you work exclusively with certified installers and maintenance professionals when installing, inspecting and repairing valves. Failure to do so can put the longevity of the medical gas valves at risk and lead to compliance failures. This failure can also cause health and safety dangers.
Accreditations from the National Inspection Testing Certification (NITC), Medical Gas Management (MGM), or Medical Equipment Training and Certification (METC) may be considered acceptable, depending on which state you operate in. Environmental & Medical Gas Services (EMGS), Airgas Medical Services (AMS), and Medical Gas Testing & Certification (MGTC) are examples of other bodies that are permitted to offer accreditation in some jurisdictions.
Just remember that different states will have their own requirements. It’s vital to check with your local authority to understand the specific requirements in your state
Schedule Regular Maintenance Checks
Make a maintenance timetable for your facility, ensuring that no inspections and regular repairs are missed. One of the key dangers when using medical oxygen valves or other medical gas valves is complacency. The valve gets checked, it’s working just fine, and everyone relaxes, possibly forgetting to schedule another assessment. If the valve starts to malfunction, this might not get noticed until it’s too late.
Setting a schedule – and sticking to this schedule – will eliminate this danger. Maintenance is not about checking up on something when you believe there is a problem. Instead, it’s about proactive checks and assessments that catch problems with the gas tank valve before they become serious.
Retain All of Your Documentation
You will need to document everything you do in relation to your medical gas valves. This may be a regulatory requirement in your area. For example, you’ll need to officially sign off on all inspections and replacement work, retaining this documentation in a safe place for future reference. You may also need full equipment inventories that you can make available to inspectors and other third parties when required.
Maintaining paper records can be difficult and inefficient. With this in mind, it may be useful to back up your documentation stores by scanning physical documents and saving them to a secure and well-organized cloud storage location. This will make it much easier to refer to your documents in the future.
Ensure Everyone Understands Their Roles, Responsibilities, and Limitations
Many of the medical professionals in your facility or healthcare institution are going to be using gas tank valves to one extent or another. Some may be handling these valves directly, replacing them when required, while others will simply be operating the gas tank’s opening and closing mechanism. What is important is that each and every member of your team understands how they should be carrying out these tasks.
Training can help to make sure that everyone has the knowledge they need to utilize equipment in a safe and reliable manner. As well as knowing how to fulfill their daily roles, individuals need to be aware of their limitations. For instance, if they are not qualified to carry out maintenance tasks, then they should know not to do so. Therefore, devise a protocol of notification so that the right people are alerted in the event of a fault. This minimizes the risk of error during inspection and maintenance.
Conduct Regular Refreshment Training
Communication is key when it comes to safe practice in this sort of environment, particularly when it comes to medical valves. Foster a culture in which personnel feel comfortable asking questions and requesting help so that they know where to go if they require any assistance.
Regular refreshment meetings and training are also factors here. Everyone has to be up to date on the latest best practices, ensuring optimal health and safety of everyone on the site and maximum longevity for the gas tank valves and other components themselves. If new regulations and best practices emerge, you’ll certainly need to hold a meeting and/or training session about this, but it’s a good idea to hold regular refreshment sessions even if there are no such changes.
Putting Patient Safety and Care Quality First – Every Time
Budgetary concerns have a habit of sneaking up on us when we least expect it, and this can lead to significant cost concerns for the managers of medical facilities and institutions. In turn, these management teams want to extend the lifespan of their equipment as much as possible, maximizing return on investment. However, this cannot come at the expense of care quality and the health and safety of patients. While keeping valves well-maintained and extending their lifespan does support these outcomes, it’s also important to keep the maximum Reasonable Usable Lifetime in mind.